Embark on a captivating exploration of the rock pocket mouse worksheet answers, revealing the fascinating world of these diminutive desert inhabitants. Their unique adaptations, intricate life cycles, and ecological significance await your discovery in this comprehensive guide.
From their rocky hideouts to their seed-dispersing habits, the rock pocket mouse unveils a compelling tale of survival and ecological balance. Prepare to delve into the depths of their existence, unraveling the secrets that make them an integral part of their arid ecosystem.
Rock Pocket Mouse Characteristics
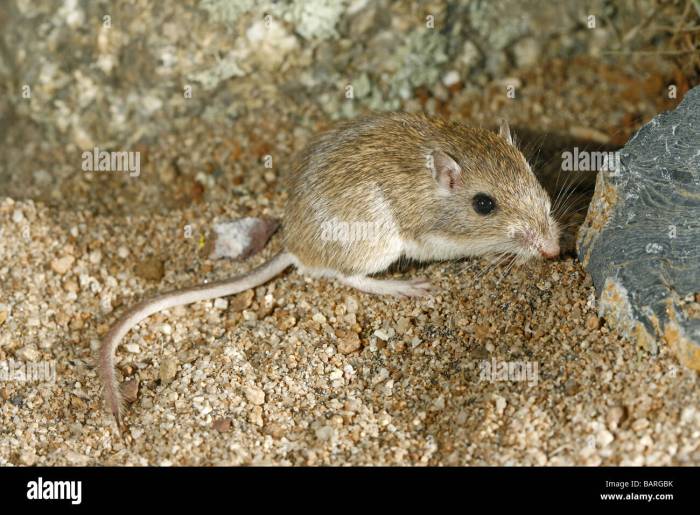
The rock pocket mouse ( Chaetodipus intermedius) is a small rodent found in the rocky areas of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. They are well-adapted to their rocky habitat, with physical attributes and behaviors that allow them to survive in this challenging environment.
Physical Attributes
Rock pocket mice are small, with a body length of 6-9 cm and a tail length of 7-10 cm. They have a sandy brown or gray coat, with a white belly. Their fur is short and dense, which helps to insulate them from the cold desert nights.
Rock pocket mice have large eyes and ears, which help them to detect predators and prey in their rocky habitat. They also have long, thin tails that they use for balance when climbing rocks.
Behaviors
Rock pocket mice are nocturnal, meaning that they are active at night. They spend the day hiding in crevices or under rocks, and come out at night to forage for food. They are omnivorous, and their diet consists of seeds, insects, and small vertebrates.
Rock pocket mice are also very good climbers, and they use their long tails to help them balance when they are climbing rocks.
Habitat, Rock pocket mouse worksheet answers
Rock pocket mice are found in rocky areas, such as canyons, mesas, and deserts. They prefer habitats with plenty of crevices and hiding places, where they can escape from predators. Rock pocket mice are also found in areas with a lot of vegetation, which provides them with food and shelter.
Adaptations
Rock pocket mice have several adaptations that help them to survive in their rocky habitat. Their sandy brown or gray coat helps them to camouflage themselves from predators. Their large eyes and ears help them to detect predators and prey in their rocky habitat.
Their long, thin tails help them to balance when they are climbing rocks. And their omnivorous diet allows them to eat a variety of foods, which is important in a habitat where food can be scarce.
Rock Pocket Mouse Life Cycle: Rock Pocket Mouse Worksheet Answers
The rock pocket mouse has a relatively short lifespan, with most individuals living for less than two years. They reach sexual maturity at around three months of age and typically breed throughout the year, although there may be some seasonal variation.
Mating and Breeding Habits
Rock pocket mice are monogamous, meaning they typically mate with only one partner for life. They form long-term pair bonds and defend their territories against other mice. During the breeding season, males will court females by performing a series of courtship displays, including chasing, grooming, and vocalizations.
Once a pair has bonded, they will mate and the female will give birth to a litter of two to six young after a gestation period of about 25 days.
Life Cycle Stages
Rock pocket mice go through a series of life cycle stages, from birth to adulthood.
Neonates
Newborn rock pocket mice are altricial, meaning they are born helpless and rely on their parents for care. They are born with their eyes closed and their fur is sparse. They nurse from their mother for several weeks until they are able to eat solid food.
Juveniles
Juvenile rock pocket mice begin to explore their surroundings and learn to forage for food at around three weeks of age. They gradually become more independent and begin to wean from their mother’s milk.
Subadults
Subadult rock pocket mice are sexually mature but have not yet reached their full adult size. They typically disperse from their natal territory and establish their own territories.
Adults
Adult rock pocket mice are fully grown and have reached sexual maturity. They typically mate and breed throughout the year and may produce multiple litters.
Factors Influencing Population Dynamics
The population dynamics of rock pocket mice are influenced by a number of factors, including:
Habitat availability
Rock pocket mice require rocky habitats with plenty of crevices and hiding places. The availability of suitable habitat can limit their population size.
Food availability
Rock pocket mice primarily eat seeds, insects, and other small invertebrates. The availability of food can fluctuate depending on the season and the availability of resources.
Predation
Rock pocket mice are preyed upon by a variety of predators, including snakes, owls, and coyotes. Predation can limit their population size and distribution.
Disease
Rock pocket mice can be infected by a variety of diseases, including hantavirus and plague. Disease outbreaks can cause significant population declines.
Climate change
Climate change is predicted to have a significant impact on the habitat and distribution of rock pocket mice. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns could make their current habitats less suitable and could lead to population declines.
Rock Pocket Mouse Interactions
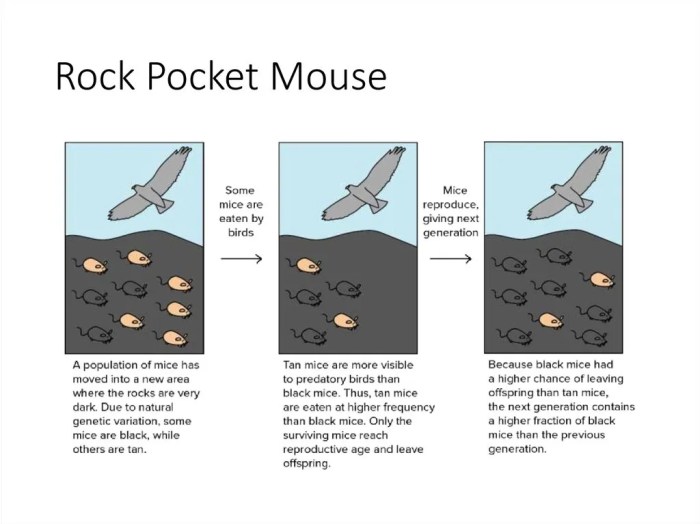
Rock pocket mice play multifaceted roles in their ecosystems, acting as both consumers and contributors to their environment. They interact with predators, prey, and plants, shaping the ecological balance of their habitats.
Their interactions with predators and prey highlight their position within the food chain. As consumers, they feed on seeds, insects, and other small invertebrates. By controlling insect populations, they indirectly benefit plants and contribute to ecosystem stability. As prey, they are hunted by snakes, owls, and other predators, providing sustenance and maintaining predator-prey dynamics.
Importance in Seed Dispersal
Rock pocket mice are crucial seed dispersers, contributing to plant diversity and vegetation growth. They collect and cache seeds in underground burrows, which serve as seed banks for future plant growth. This behavior promotes seed germination, increases plant populations, and ensures genetic diversity within plant communities.
Role in Nutrient Cycling
Their burrowing activities and seed caching contribute to nutrient cycling. By digging burrows, they aerate the soil, improving drainage and nutrient availability for plants. Additionally, their cached seeds decompose over time, releasing nutrients back into the soil, enriching the ecosystem and supporting plant growth.
Rock Pocket Mouse Conservation

Rock pocket mice face several threats to their populations, including habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation. Habitat loss occurs when natural areas are converted to other uses, such as agriculture, development, or mining. Fragmentation occurs when habitats are broken up into smaller pieces, which can make it difficult for mice to move between them.
Degradation occurs when habitats are damaged or polluted, which can make them less suitable for mice.Conservation measures have been implemented to protect rock pocket mouse habitats. These measures include:
- Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife refuges, to provide safe havens for mice.
- Managing grazing and other activities to reduce habitat degradation.
- Restoring degraded habitats to improve their quality for mice.
Preserving rock pocket mice is important for ecological balance. Mice play a vital role in the ecosystem by dispersing seeds, controlling insect populations, and providing food for predators. Their presence helps to maintain the health and diversity of the ecosystem.
Rock Pocket Mouse Research

Research on the rock pocket mouse has focused on understanding its behavior, ecology, and genetics. Researchers have employed various methods to study this species, including field observations, laboratory experiments, and genetic analysis.
Behavioral Studies
- Observational studies have documented the rock pocket mouse’s social behavior, including territoriality, mating systems, and parental care.
- Laboratory experiments have investigated the cognitive abilities of rock pocket mice, such as their spatial memory and problem-solving skills.
Ecological Studies
- Field studies have examined the rock pocket mouse’s habitat use, foraging behavior, and interactions with other species.
- Population monitoring programs have tracked changes in rock pocket mouse populations over time, providing insights into the species’ response to environmental factors.
Genetic Studies
- Genetic analysis has been used to identify distinct populations of rock pocket mice and study their genetic diversity.
- Comparative genomics has allowed researchers to compare the rock pocket mouse’s genome to other species, providing insights into its evolutionary history and adaptations.
Research findings on the rock pocket mouse have contributed significantly to our understanding of this species’ unique biology and its role in the ecosystem. They have also informed conservation efforts aimed at protecting and managing rock pocket mouse populations.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary food source of the rock pocket mouse?
Seeds, insects, and vegetation
How do rock pocket mice store water?
They obtain water from their food and do not require additional sources
What is the average lifespan of a rock pocket mouse?
Approximately 2-3 years in the wild