Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane, a fundamental process in the chemical industry. This reaction converts acetylene, a versatile starting material, into ethane, a crucial feedstock for various applications. Understanding the mechanism, catalysts, reaction conditions, and industrial significance of this hydrogenation process is essential for chemists and engineers.
Acetylene, with its triple bond, undergoes hydrogenation in the presence of a catalyst to yield ethane, a saturated hydrocarbon. This transformation plays a vital role in the production of polyethylene, a widely used plastic, and other valuable chemicals.
Background and Overview

Acetylene is a colorless, highly flammable gas with a distinctive odor. It is the simplest alkyne, containing two carbon atoms triple-bonded to each other. Ethane, on the other hand, is a colorless, odorless gas that is the second member of the alkane series.
It consists of two carbon atoms bonded to each other by a single bond and six hydrogen atoms.
The process of hydrogenation involves the addition of hydrogen to a compound. In the case of acetylene, hydrogenation results in the formation of ethane.
Reaction Mechanism: Acetylene Is Hydrogenated To Form Ethane
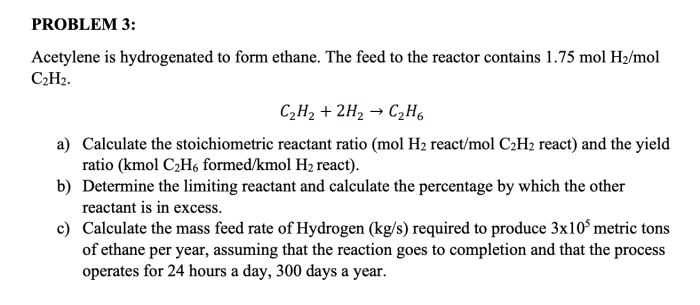
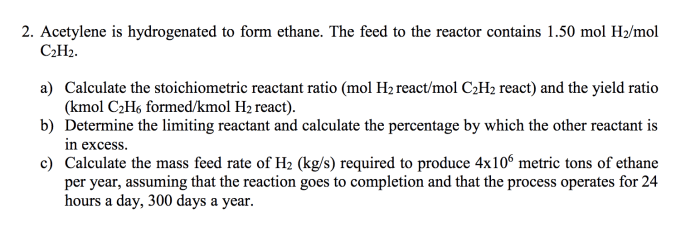
The hydrogenation of acetylene to form ethane occurs in two steps:
- In the first step, acetylene reacts with hydrogen to form ethylene. This reaction is catalyzed by a metal catalyst, such as palladium or platinum.
- In the second step, ethylene reacts with another molecule of hydrogen to form ethane. This reaction is also catalyzed by a metal catalyst.
The overall chemical equation for the hydrogenation of acetylene to form ethane is:
Catalysts, Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane
The most common catalysts used in the hydrogenation of acetylene are palladium and platinum. These metals are effective at breaking the triple bond in acetylene and facilitating the addition of hydrogen.
Reaction Conditions
The optimal reaction conditions for the hydrogenation of acetylene are a temperature of 25-50°C and a pressure of 1-10 atm. The solvent used is typically an alcohol, such as methanol or ethanol.
Applications
The hydrogenation of acetylene to form ethane is an important industrial process. Ethane is used as a raw material in the production of a variety of products, including polyethylene, ethylene oxide, and vinyl chloride.
Safety Considerations
Acetylene is a highly flammable gas and can form explosive mixtures with air. It is important to take proper safety precautions when working with acetylene, including using appropriate ventilation and avoiding open flames.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of the hydrogenation of acetylene?
The hydrogenation of acetylene is a crucial process for producing ethane, a vital feedstock for the production of polyethylene, a widely used plastic.
What catalysts are commonly used in the hydrogenation of acetylene?
Common catalysts for the hydrogenation of acetylene include palladium, platinum, and nickel.
What are the optimal reaction conditions for the hydrogenation of acetylene?
The optimal reaction conditions for the hydrogenation of acetylene involve moderate temperatures, elevated pressures, and the presence of a suitable catalyst.