Labeling 2-2 Reference Manual Phlebotomy, an indispensable guide in the realm of blood collection, unravels the complexities of specimen labeling, empowering healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to ensure accurate and reliable laboratory results. This comprehensive manual provides a roadmap for navigating the intricacies of specimen collection, handling, and rejection criteria, ensuring the highest standards of safety and quality control.
Phlebotomy Reference Manual Basics

A phlebotomy reference manual is an essential tool for phlebotomists, providing comprehensive information and guidance on all aspects of phlebotomy practice. It serves as a valuable resource for both novice and experienced phlebotomists, ensuring accurate and efficient blood collection and handling.
Typically, a phlebotomy reference manual includes sections covering the following topics:
- Basic phlebotomy techniques
- Specimen collection and handling
- Specimen labeling and identification
- Safety protocols and quality control measures
- Troubleshooting and error prevention
To effectively use a reference manual in phlebotomy practice, phlebotomists should:
- Familiarize themselves with the manual’s organization and content.
- Use the manual as a quick reference guide for specific procedures or information.
- Stay updated on any revisions or additions to the manual.
- Seek additional training or support if needed to fully understand the manual’s content.
Labeling Specimen Containers: Labeling 2-2 Reference Manual Phlebotomy

Proper labeling of specimen containers is crucial in phlebotomy to ensure accurate identification and tracking of patient samples. Mislabeled specimens can lead to errors in testing and patient care.
There are various types of specimen labels used in phlebotomy, including:
- Preprinted labels with patient demographics
- Handwritten labels
- Barcoded labels
To correctly label specimen containers, phlebotomists should:
- Use legible handwriting or print clearly on preprinted labels.
- Include the following information on the label: patient’s full name, date of birth, date and time of collection, and specimen type.
- Verify the patient’s identity before labeling the specimen.
- Double-check the accuracy of the information on the label.
Common labeling errors to avoid include:
- Illegible or incomplete information
- Misspellings or incorrect patient demographics
- Incorrect specimen type
- Lack of a signature or initials
Specimen Collection and Handling
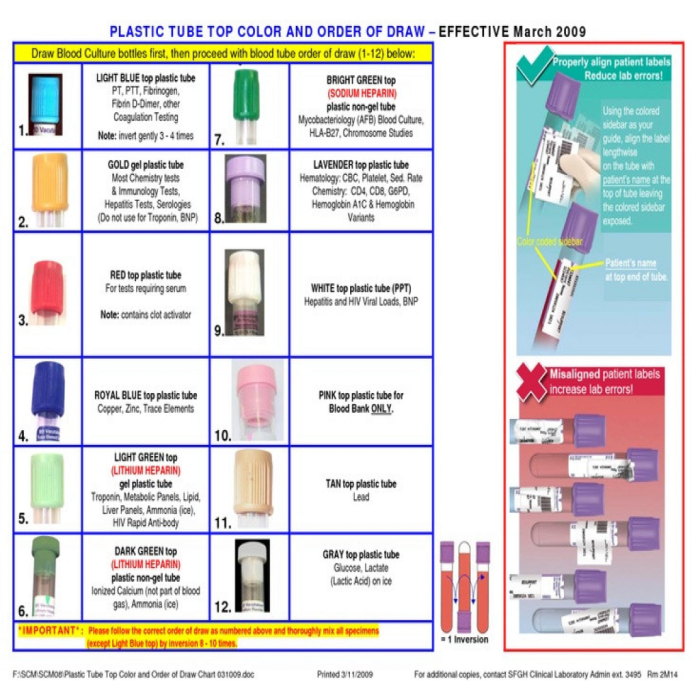
Proper collection and handling of blood specimens are essential to ensure the integrity of the sample and the accuracy of test results. Phlebotomists must adhere to specific procedures to maintain specimen quality.
The different types of blood collection tubes used in phlebotomy include:
- Vacutainer tubes with various additives (e.g., EDTA, heparin, sodium citrate)
- Serum tubes
- Plasma tubes
To collect and handle specimens correctly, phlebotomists should:
- Use the appropriate blood collection tube for the test being ordered.
- Fill the tube to the correct volume.
- Mix the specimen thoroughly according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Centrifuge the specimen if necessary.
- Transport the specimen to the laboratory promptly and according to established protocols.
Maintaining specimen integrity during collection and transport is crucial. Phlebotomists should avoid:
- Hemolysis (rupture of red blood cells)
- Lipemia (presence of excessive fats in the blood)
- Clot formation
- Bacterial contamination
Specimen Rejection Criteria
Specimens may be rejected for testing due to various reasons, such as improper labeling, insufficient volume, or contamination. Identifying and handling rejected specimens correctly is essential to prevent errors and ensure patient safety.
The different types of specimen rejection criteria include:
- Incorrect or missing patient identification
- Insufficient specimen volume
- Hemolysis or lipemia
- Clot formation
- Bacterial contamination
- Incorrect specimen type
To identify and handle rejected specimens, phlebotomists should:
- Inspect the specimen for any visible defects or irregularities.
- Verify the patient’s identity and the accuracy of the specimen label.
- Notify the healthcare provider if a specimen is rejected.
- Document the reason for rejection and dispose of the specimen according to established protocols.
Common rejection criteria and how to avoid them:
| Rejection Criteria | How to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Incorrect patient identification | Verify patient’s identity before labeling the specimen. |
| Insufficient specimen volume | Collect the correct volume of blood into the appropriate tube. |
| Hemolysis | Use proper venipuncture technique and handle the specimen gently. |
Safety and Quality Control
Safety and quality control are paramount in phlebotomy practice to protect both patients and healthcare workers and ensure the accuracy and reliability of test results.
Important safety protocols and quality control measures in phlebotomy include:
- Universal precautions to prevent the transmission of infectious diseases
- Proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Regular calibration and maintenance of equipment
- Quality control checks on reagents and supplies
- Documentation of all procedures and incidents
To maintain a safe and quality-controlled work environment, phlebotomists should:
- Follow all safety protocols and wear appropriate PPE.
- Handle and dispose of sharps and biohazardous materials safely.
- Report any accidents or incidents immediately.
- Participate in continuing education and training to stay up-to-date on best practices.
Common safety hazards and quality control issues and how to mitigate them:
| Safety Hazard/Quality Control Issue | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Needle stick injuries | Use proper venipuncture technique and dispose of sharps safely. |
| Specimen contamination | Follow proper specimen collection and handling procedures. |
Key Questions Answered
What is the purpose of specimen labeling in phlebotomy?
Specimen labeling plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate patient identification, specimen integrity, and timely analysis.
What are the common types of specimen labels used in phlebotomy?
Common specimen labels include self-adhesive labels, wristbands, and electronic labels, each serving specific purposes.
What are the key considerations for avoiding labeling errors?
Accuracy, completeness, and legibility are paramount in specimen labeling to prevent misidentification and ensure reliable test results.