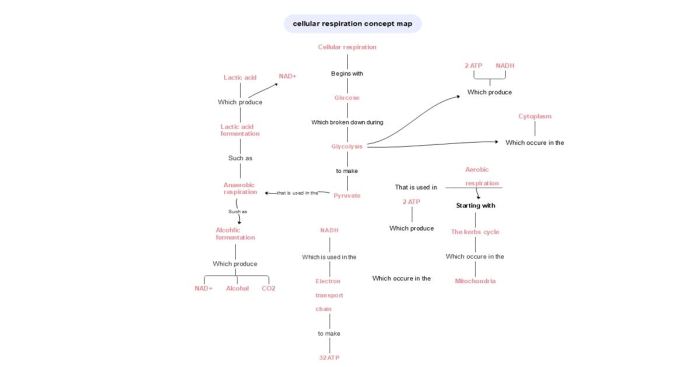
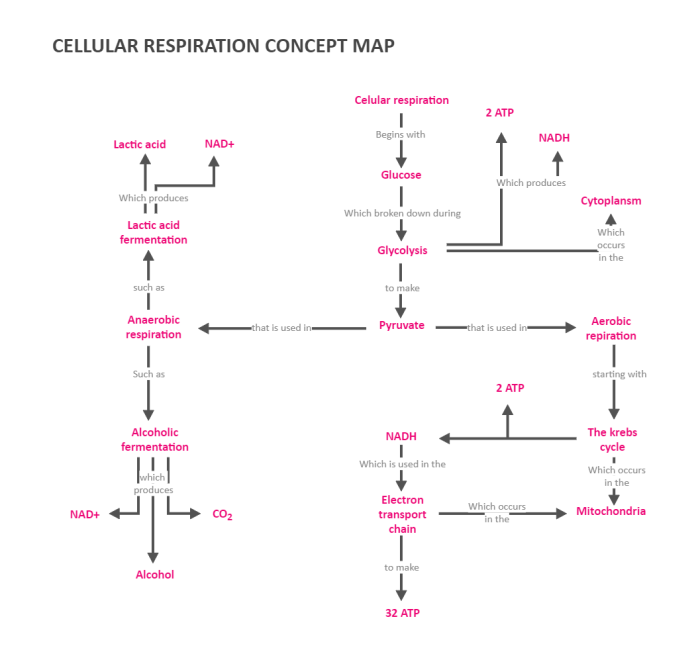
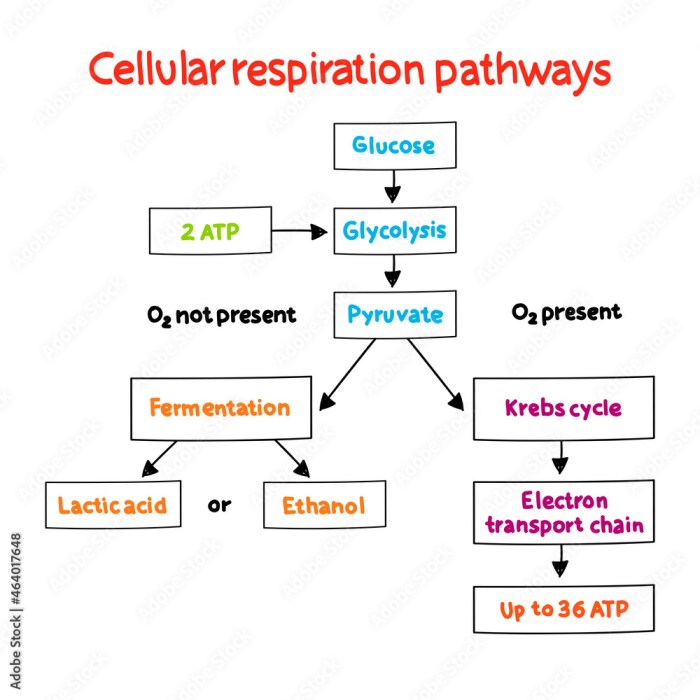
Practice cellular respiration concept map answers – Embark on an exploration of cellular respiration with our comprehensive concept map answers. Delving into the intricate processes that fuel life, we unravel the mechanisms that govern energy production and sustain the vitality of all living organisms.
Cellular respiration, the cornerstone of energy metabolism, unveils its secrets as we dissect its stages, from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation. Discover the role of ATP, the cellular energy currency, and witness the intricate interplay of enzymes and cofactors that orchestrate this vital process.
Cellular Respiration Overview: Practice Cellular Respiration Concept Map Answers
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. This process is essential for the survival of all living organisms because ATP serves as the main energy currency for cells.
Cellular respiration occurs in four main stages:
- Glycolysis
- Pyruvate oxidation
- Citric acid cycle
- Oxidative phosphorylation
ATP plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by providing the energy required for various cellular processes, such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and active transport of molecules across cell membranes.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. It involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar molecule, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound.
During glycolysis, glucose is phosphorylated and then split into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P). G3P is further oxidized and phosphorylated to produce pyruvate, along with a net gain of two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH.
The regulation of glycolysis is complex and involves multiple enzymes and feedback mechanisms. Key regulatory enzymes include phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) and pyruvate kinase (PK).
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate oxidation is the second stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. It involves the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, a two-carbon compound.
The key enzyme in pyruvate oxidation is pyruvate dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. This reaction produces acetyl-CoA, NADH, and CO2.
The regulation of pyruvate oxidation is primarily controlled by the availability of NAD+ and acetyl-CoA. High levels of NADH inhibit pyruvate dehydrogenase, while high levels of acetyl-CoA activate it.
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is the third stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
The citric acid cycle involves a series of nine enzymatic reactions that result in the oxidation of acetyl-CoA to produce CO2, NADH, FADH2, and ATP.
The regulation of the citric acid cycle is complex and involves multiple feedback mechanisms. Key regulatory enzymes include citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
Oxidative Phosphorylation, Practice cellular respiration concept map answers
Oxidative phosphorylation is the fourth and final stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Oxidative phosphorylation involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen through a series of electron carriers, known as the electron transport chain. This process generates a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is used to drive the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase.
The regulation of oxidative phosphorylation is primarily controlled by the availability of NADH and FADH2. High levels of NADH and FADH2 stimulate oxidative phosphorylation, while low levels inhibit it.
FAQ Explained
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert biochemical energy from nutrients into ATP, the universal energy currency of life.
What are the four main stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Where does glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.